Discover how to use the Chaikin Volatility Indicator to spot breakouts, manage risks, and improve your trading strategy effectively.

Introduction: Understanding Volatility in Trading
Why Volatility Matters in Financial Markets
Volatility reflects price movement intensity, signaling risk and potential profit in trading. Understanding volatility helps traders identify market opportunities and adjust strategies.
Key takeaway: Higher volatility often means greater opportunities, but it also increases risk.
What Is the Chaikin Volatility Indicator (CVI)?
The Chaikin Volatility Indicator measures changes in market volatility by comparing high-low ranges over time. Developed by Marc Chaikin, it’s widely used to spot potential breakout points and market reversals.
Key takeaway: CVI is a technical tool to anticipate market behavior shifts.
Why Use the Chaikin Volatility Indicator?
The CVI helps traders prepare for price breakouts and trend changes by analyzing fluctuations in volatility. It doesn’t provide directional cues, so combining it with other indicators is key for effective trading.
Key takeaway: CVI simplifies identifying periods of heightened or reduced market activity.
What This Guide Covers
This guide offers a comprehensive look at CVI, including its formula, use cases, and step-by-step trading strategies. You’ll also learn its strengths, weaknesses, and practical examples for implementation.
Key takeaway: Gain practical insights into mastering the Chaikin Volatility Indicator.
For more on technical indicators and their applications, check out Investopedia’s Guide to Technical Indicators.

Formula for the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
Understanding the Chaikin Volatility Indicator Formula
The formula for the Chaikin Volatility Indicator (CVI) is:
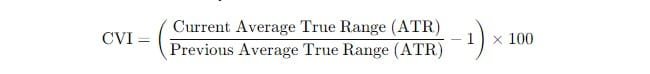
This formula measures the percentage change in volatility over a specified time period by comparing the current ATR to a previous ATR.
Key takeaway: CVI quantifies volatility changes as a percentage, making it easier to identify market activity shifts.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the CVI Formula
1. Calculate the True Range (TR):
True Range is the largest of the following:
- Current high minus current low.
- Current high minus previous close.
- Current low minus previous close.
Key takeaway: TR captures the most significant price movement between periods.
2. Compute the Average True Range (ATR):
ATR is a moving average of the True Range over a specific period (e.g., 10 or 20 days). It smooths out daily volatility spikes.
Key takeaway: ATR represents average price range movement over time, aiding consistent volatility measurement.
3. Apply the CVI Formula:
Divide the current ATR by the previous ATR, subtract 1, and multiply by 100 to express the result as a percentage.
Key takeaway: The CVI highlights the relative change in volatility, helping traders spot breakouts or trend shifts.
How Parameter Settings Affect CVI Responsiveness
Short Lookback Periods (e.g., 10 days):
These settings make the CVI more sensitive, reacting quickly to short-term volatility changes. However, this may lead to false signals in choppy markets.Long Lookback Periods (e.g., 20 days):
These provide smoother signals, reducing noise but potentially delaying reactions to sudden market changes.
Key takeaway: Short periods offer faster signals; longer periods enhance stability and reduce noise.
Tips for Customizing CVI Settings
- Experiment with different periods to align the CVI’s behavior with your trading strategy.
- Use shorter periods for intraday trading and longer ones for swing trading or trend analysis.
For more details on ATR and its applications, refer to Investopedia’s Guide on Average True Range (ATR).

When and How to Use the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
When to Use the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
Ideal Market Conditions for Using CVI
The Chaikin Volatility Indicator (CVI) is particularly effective in identifying key market conditions:
- Pre-Breakout Scenarios: Rising CVI values often precede significant price movements, indicating heightened market activity.
- Trending Markets: In strong trends, CVI can help confirm volatility spikes that signal trend continuation.
Key takeaway: Use CVI in dynamic markets, especially when anticipating breakouts or confirming ongoing trends.
Suitable Assets for CVI
The CVI works well across various asset classes, including:
- Stocks: Spot price breakout opportunities during earnings announcements or news events.
- Forex: Identify periods of high volatility in currency pairs before major economic events.
- Commodities: Detect trend shifts in volatile markets like crude oil or gold.
Key takeaway: CVI is versatile and effective in stocks, forex, and commodity trading.
How to Use the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
Rising CVI Values: A Signal of Increasing Volatility
When CVI values rise, it indicates increasing volatility, often signaling a potential price breakout. Pair it with a trend indicator (e.g., Moving Averages or ADX) to confirm breakout direction.
Key takeaway: Rising CVI values are early warning signs of significant price movements.
Decreasing CVI Values: A Signal of Decreasing Volatility
A falling CVI suggests reduced volatility, typically after a strong trend. This signals a consolidation phase or reduced trading opportunities.
Key takeaway: Decreasing CVI values often indicate stabilization or trend exhaustion.
Examples of Market Scenarios
1. Trend Reversals:
Rising CVI during prolonged low volatility periods may indicate an upcoming trend reversal. For example, a stock consolidating within a tight range suddenly shows increasing CVI values, hinting at a breakout.
2. Consolidation Periods:
When CVI decreases after a strong trend, the market may enter a sideways phase, allowing traders to reassess strategies.
Key takeaway: Understand market scenarios like breakouts or consolidations to use CVI effectively.
Practical Tips for Using CVI in Trading
- Combine CVI with directional indicators like MACD or RSI for better trade confirmation.
- Avoid over-reliance on CVI in low-liquidity markets to reduce false signals.
For further reading, explore TradingView’s Guide on Volatility Indicators.

Can the Chaikin Volatility Indicator Be Used Alone?
Strengths of the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
1. Excellent for Gauging Volatility Shifts
The Chaikin Volatility Indicator (CVI) excels at identifying periods of rising or falling volatility. This helps traders anticipate significant price changes before they occur.
Key takeaway: CVI provides early warning signals for potential breakouts or trend shifts.
2. Helps Anticipate Significant Price Movements
By focusing on volatility rather than price direction, the CVI gives traders a heads-up on possible market activity. It’s particularly useful during quiet market periods that precede major moves.
Key takeaway: CVI is a proactive tool for preparing trading strategies.
Weaknesses of the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
1. Lacks Directional Information
CVI does not indicate the direction of price movements. Traders must pair it with other indicators to confirm trends or reversals.
Key takeaway: Use CVI with trend or momentum indicators for directional clarity.
2. May Generate False Signals in Choppy Markets
In low-liquidity or sideways markets, CVI may produce false signals, leading to unnecessary trades. This is common when small price changes trigger volatility spikes.
Key takeaway: Avoid relying solely on CVI in unpredictable or low-volume markets.
Complementary Indicators for Chaikin Volatility
1. Trend Indicators
- Moving Averages (MA): Confirm the direction of price trends when CVI shows rising volatility.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Helps validate breakouts and trend continuations.
2. Volume Indicators
- Chaikin Money Flow (CMF): Measures buying or selling pressure to align volatility with volume trends.
- On-Balance Volume (OBV): Highlights whether volume supports price movement.
3. Momentum Indicators
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Identifies overbought or oversold conditions alongside volatility changes.
- Stochastic Oscillator: Pinpoints momentum shifts in trending or consolidating markets.
Key takeaway: Combining CVI with these indicators provides a more comprehensive market analysis.
Example: Using CVI with Other Indicators
Imagine a stock showing rising CVI values. Adding a MACD crossover confirms a bullish trend, while a high RSI value warns of potential overbought conditions. This combination ensures you act on reliable signals while minimizing false entries.
For further insights, explore StockCharts’ Guide to Technical Indicators.

Step-by-Step Guide to Trade with the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
A Simple Trading Strategy Using the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
Step 1: Identify Rising Volatility with the CVI
Monitor the Chaikin Volatility Indicator (CVI) for an upward spike, signaling increased volatility. Rising CVI values often indicate potential breakouts or significant price movements.
Key takeaway: Rising CVI is a precursor to market activity, ideal for spotting trading opportunities.
Step 2: Confirm Direction with a Trend or Momentum Indicator
Pair CVI with indicators like Moving Averages (MA) or Relative Strength Index (RSI) to confirm the price direction.
- Uptrend: Rising CVI with prices above the 20-day MA suggests a bullish breakout.
- Downtrend: Rising CVI with RSI below 30 may signal a bearish breakdown.
Key takeaway: Combining CVI with directional indicators ensures reliable trade signals.
Step 3: Use Risk Management Tools
Implement risk management techniques like:
- Stop-Loss Orders: Place stop-losses below support levels (bullish trades) or above resistance (bearish trades).
- Position Sizing: Allocate a percentage of your capital to minimize risks.
Key takeaway: Proper risk management protects your capital and minimizes trading losses.
Example: Bullish and Bearish Trades with CVI
Bullish Breakout Trade
- CVI spikes upward, signaling rising volatility in a consolidating stock.
- Price breaks above resistance, confirmed by a MACD crossover.
- Enter a long trade with a stop-loss just below the breakout level.
Bearish Breakdown Trade
- CVI rises as a stock approaches a key support level.
- RSI drops below 30, confirming bearish momentum.
- Enter a short trade with a stop-loss slightly above the support level.
Key takeaway: Bullish and bearish examples illustrate how to apply CVI in practical trading scenarios.
Tips for Fine-Tuning Your Strategy
- Adjust Timeframes: Use shorter timeframes (e.g., 5-minute charts) for intraday trading and longer ones (e.g., daily charts) for swing trades.
- Combine Multiple Indicators: Use volume indicators like Chaikin Money Flow (CMF) for additional confirmation.
- Test Strategies in Demo Accounts: Refine your strategy in a risk-free environment before trading live.
For a more detailed trading framework, check out TradingView’s Strategy Ideas.

Example for Chaikin Volatility Indicator
Case Study Using Historical Data
Example 1: A Bullish Breakout with Rising CVI
In this case, a stock consolidated for several weeks, forming a tight price range. During this period, the Chaikin Volatility Indicator (CVI) displayed low, stable values, reflecting limited price movement. Suddenly, the CVI spiked, indicating rising volatility.
- Observation: The price broke above a resistance level shortly after the CVI increase.
- Confirmation: A MACD crossover occurred simultaneously, confirming bullish momentum.
- Outcome: Traders who entered early benefited from the breakout and captured substantial gains.
Key takeaway: Rising CVI values often precede breakout opportunities, especially in consolidating markets.
Example 2: Low CVI Values Indicating Reduced Opportunities
A currency pair experienced prolonged low volatility, with the CVI showing consistently decreasing values. The price moved sideways with minimal fluctuations, creating a low-risk, low-reward environment.
- Observation: The low CVI values indicated limited trading opportunities due to market inactivity.
- Action: Traders avoided unnecessary trades, waiting for a clear signal or volatility spike.
- Outcome: This helped prevent capital erosion from unproductive trades.
Key takeaway: Low CVI values signal quiet markets, ideal for standing aside until better opportunities emerge.
Lessons from the Examples
- Be Patient: Wait for CVI confirmation before entering trades. Acting too early can lead to losses.
- Use Complementary Indicators: Enhance the reliability of CVI signals with tools like MACD, RSI, or Moving Averages.
- Adapt to Market Conditions: Recognize when to act (breakouts) and when to pause (low volatility periods).
For further insights into using technical indicators effectively, explore Investopedia’s Trading Strategies Guide.

When Can You Turn a Profit with Chaikin Volatility Indicator?
Realistic Profit Expectations with the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
Understanding Profit Potential Based on Historical Performance
The Chaikin Volatility Indicator (CVI) identifies volatility shifts but does not guarantee profits. Historical data shows that traders who combine CVI with complementary tools—like trend indicators or volume analysis—maximize their profitability.
- Breakouts: Rising CVI values before price surges often lead to profitable trades.
- Trend Continuation: Increasing CVI during a strong trend confirms ongoing momentum.
Key takeaway: Expect consistent results only when using CVI within a disciplined, multi-indicator trading strategy.
The Importance of Disciplined Risk Management
Why Risk Management Is Crucial
Even with accurate CVI signals, unpredictable market events can lead to losses. Employing strict risk management tools ensures long-term profitability:
- Stop-Loss Orders: Protect your capital during volatile reversals.
- Position Sizing: Allocate a fixed percentage of your portfolio to each trade.
Key takeaway: Protect profits and minimize losses by incorporating robust risk management practices.
Confirmation Signals for Better Accuracy
Pair CVI with indicators like MACD or RSI to validate entry and exit points. Avoid trading solely based on CVI spikes.
Key takeaway: Confirmation tools reduce false signals and improve trading precision.
Common Scenarios Where CVI Leads to Profitable Trades
1. Breakouts in Consolidating Markets
Rising CVI during consolidation often signals a breakout. Pair this with a directional indicator to capture early gains.
- Example: A stock consolidates with flat CVI values, then spikes alongside a price breakout.
2. Trend Continuation During High Volatility
An increasing CVI during a strong uptrend confirms the trend is likely to continue. Combine with Moving Averages for precise entries.
- Example: A forex pair shows rising CVI and remains above its 50-day MA.
3. Reversal Signals After a Prolonged Trend
Sudden CVI spikes at the end of a prolonged trend may indicate a reversal. Use RSI or stochastic oscillators for additional confirmation.
Key takeaway: Profitable trades often arise in scenarios involving breakouts, trends, or reversals, guided by CVI.
Actionable Tips for Profitability
- Backtest Your Strategy: Validate CVI-based setups using historical data before applying them in live markets.
- Be Selective: Focus on high-probability setups, avoiding trades in choppy or low-liquidity markets.
- Stay Informed: Adapt to evolving market conditions by regularly reviewing your strategy.
For further guidance on maximizing trading performance, visit DailyFX’s Guide to Trading Volatility.

Advantages and Disadvantages of the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
Advantages of the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
1. Simple and Easy to Understand
The Chaikin Volatility Indicator (CVI) is straightforward, making it accessible for traders of all experience levels.
- Calculation Clarity: The CVI formula relies on well-known metrics like the Average True Range (ATR), simplifying adoption.
- Visual Representation: The CVI’s rising and falling values clearly reflect volatility changes in any market.
Key takeaway: CVI’s simplicity ensures accessibility while offering actionable insights into market volatility.
2. Early Warning for Breakout Scenarios
The CVI effectively detects volatility increases, often preceding significant price breakouts.
- Use Case: Spikes in CVI often highlight key moments to anticipate market shifts.
- Improved Timing: Early signals allow traders to prepare for entry or exit opportunities.
Key takeaway: CVI acts as an early alarm for potential breakouts, giving traders a strategic advantage.
3. Adaptable to Various Timeframes and Markets
The CVI works seamlessly across multiple timeframes and asset classes, including stocks, forex, and commodities.
- Day Traders: Use short timeframes (e.g., 5-minute charts) for quick volatility spikes.
- Swing Traders: Analyze daily or weekly charts for longer-term trends.
Key takeaway: CVI’s versatility makes it a valuable tool for diverse trading strategies.
Disadvantages of the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
1. Not a Standalone Solution
CVI does not provide directional signals, requiring complementary indicators for accuracy.
- Limitation: Rising CVI alone cannot confirm whether price will move up or down.
- Solution: Pair with indicators like Moving Averages, RSI, or MACD to enhance decision-making.
Key takeaway: CVI needs supporting tools to generate reliable trading signals.
2. Can Be Lagging During Rapid Market Changes
The CVI may struggle to adapt to sudden market shifts, leading to delayed signals.
- Observation: Rapid reversals may occur before the CVI fully responds.
- Risk: Lagging signals can result in missed opportunities or poor trade timing.
Key takeaway: CVI is less effective during sudden market movements and requires cautious interpretation.
Balancing CVI’s Pros and Cons
While the Chaikin Volatility Indicator offers early breakout detection and versatility, it is most effective when used in combination with other tools.
For more tips on optimizing technical indicators, visit Investopedia’s Guide to Trading Indicators.

Historical Context and Evolution of the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
The Genius Behind the Indicator: Marc Chaikin
Who Is Marc Chaikin?
Marc Chaikin is a renowned technical analyst with decades of experience in financial markets. He is widely respected for creating innovative tools that simplify market analysis, including the Chaikin Money Flow (CMF) and the Chaikin Oscillator.
- Contribution: Chaikin developed indicators to analyze price trends and market strength with a focus on volume and volatility.
- Legacy: His work laid the foundation for volatility-based indicators, helping traders anticipate price movements effectively.
Key takeaway: Marc Chaikin’s contributions transformed technical analysis, offering tools that are intuitive and actionable.
For a detailed overview of Chaikin’s indicators, visit Marc Chaikin’s Official Website.
Evolution of Volatility-Based Indicators
Early Volatility Tools
Volatility analysis began with basic tools like Bollinger Bands and ATR, designed to measure market fluctuations.
- Bollinger Bands: Helped traders identify overbought and oversold conditions.
- ATR: Provided a numerical measure of price volatility over time.
Key takeaway: These early tools paved the way for more sophisticated volatility indicators like CVI.
How the Chaikin Volatility Indicator Fits In
Introduced by Chaikin, the CVI built on the ATR concept by focusing on percentage changes in volatility.
- Unique Approach: CVI measures volatility independently of price direction, making it versatile across market conditions.
- Modern Applications: The indicator is now used alongside advanced tools like MACD, RSI, and Fibonacci retracements.
Key takeaway: CVI’s innovation lies in its ability to predict volatility shifts, making it an essential tool for proactive trading.
CVI in Today’s Trading Landscape
Adapting to Market Complexity
The Chaikin Volatility Indicator has evolved to remain relevant in today’s fast-paced markets. It integrates seamlessly with algorithmic trading strategies and multi-timeframe analysis.
- Advancement: Traders now use CVI data for enhanced decision-making, combining it with AI-powered tools.
- Broad Application: From day trading to long-term investing, CVI caters to various trading styles.
For more insights into volatility indicators, explore Investopedia’s Guide to Volatility Tools.

Integration of the Chaikin Volatility Indicator with Risk Management
1. Adjusting Strategies Based on Volatility Levels
Using CVI During High and Low Volatility Periods
The Chaikin Volatility Indicator (CVI) offers crucial insights into market volatility, allowing traders to adapt their strategies.
- High Volatility: During rising CVI values, consider strategies like breakout trading or scaling back position sizes to manage risk.
- Low Volatility: When CVI values are flat or declining, adopt range-bound strategies or hold off for better setups.
Key takeaway: CVI helps traders align their strategies with the current market environment, reducing unnecessary risks.
For more on adapting to volatility, check this trading risk management guide.
2. Using CVI to Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
Dynamic Risk Adjustments with CVI
The CVI allows traders to optimize stop-loss and take-profit levels by aligning with market volatility.
- High Volatility: Wider stop-loss levels can prevent premature exits during sharp price swings.
- Low Volatility: Tighter stop-loss levels are appropriate to avoid holding during low-movement phases.
Real-Life Example
If CVI spikes before a breakout, place stop-losses beyond support or resistance to account for increased price swings.
Key takeaway: CVI enhances trade planning by aligning stop-loss and take-profit levels with market conditions.
3. Avoiding Overexposure During Volatile Periods
Managing Position Sizes with CVI Insights
CVI aids in managing exposure during volatile markets by suggesting adjustments to position sizes.
- Risk Reduction: Reduce trade sizes when CVI signals heightened volatility to limit potential losses.
- Portfolio Balance: Use CVI to diversify or rebalance investments, minimizing concentration risks during volatile periods.
Practical Tip
Combine CVI insights with tools like the Kelly Criterion to determine optimal position sizing.
Key takeaway: CVI safeguards traders from overexposure, promoting disciplined and balanced risk management.
CVI as a Risk Management Ally
The Chaikin Volatility Indicator is a powerful tool for integrating risk management into trading strategies. Its ability to signal volatility shifts ensures traders stay proactive in protecting their capital.
For more risk management strategies, visit Investopedia’s Risk Management Techniques.

Common Misinterpretations or Misuses of the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
1. Assuming Every Increase in CVI Predicts a Breakout
Misconception: Rising CVI Guarantees a Breakout
One common mistake is interpreting every CVI increase as a signal for price breakouts.
- Why It’s Misleading: CVI measures volatility but does not indicate price direction or guarantee movement magnitude.
- Reality Check: Rising CVI can reflect indecision or sharp reversals, not just breakouts.
Practical Tip
Combine CVI with trend confirmation tools like Moving Averages or MACD to verify breakout potential.
Key takeaway: CVI alone does not confirm breakouts—use it alongside complementary indicators for better accuracy.
For more on validating breakouts, visit this guide on technical indicators.
2. Ignoring Other Market Conditions
Neglecting Volume or Trend Direction
Traders often misuse CVI by overlooking critical factors like market volume and existing trends.
- Impact of Volume: Rising CVI with low volume might signal false breakouts or weak price movements.
- Trend Importance: Ignoring trend direction can lead to entering trades against the prevailing market flow.
Solution
Use CVI with volume indicators (e.g., Chaikin Money Flow) or trend tools (e.g., RSI, ADX) for a holistic view.
Key takeaway: Market context, including volume and trend, is essential for interpreting CVI signals correctly.
3. Overfitting Parameters to Specific Market Scenarios
What Is Overfitting in CVI Analysis?
Overfitting occurs when traders fine-tune CVI settings (e.g., lookback periods) to fit past data perfectly.
- Why It’s Problematic: Overfitting reduces the indicator’s adaptability, making it ineffective in real-time scenarios.
- Example: Using a 5-day lookback optimized for one stock might fail in broader market conditions.
How to Avoid Overfitting
Stick to commonly used settings like 10-day or 20-day periods, adjusting only based on significant market trends.
Key takeaway: Overfitting CVI parameters undermines reliability—use balanced settings that work across various conditions.
Mitigating Misinterpretations and Misuses
To maximize the Chaikin Volatility Indicator’s effectiveness, combine it with other tools, respect market context, and avoid over-optimization. For more best practices in technical analysis, explore Investopedia’s Trading Strategies.

FAQs and Troubleshooting for the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
1. Common Questions About Using the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
What Are the Best Settings for CVI?
The optimal settings for the Chaikin Volatility Indicator depend on your trading style and market.
- Common Parameters: The 10-day or 20-day lookback period is widely used for most assets.
- Adaptation: Shorter lookback periods (e.g., 5 days) suit intraday trading, while longer periods (e.g., 30 days) fit swing trading.
Key takeaway: Test different settings to find the balance that suits your trading goals and preferred timeframe.
Does CVI Work for All Timeframes?
Yes, the CVI is flexible and can be applied across different timeframes.
- Intraday Trading: Use shorter timeframes (e.g., 5-minute or 15-minute charts) for quick decision-making.
- Long-Term Trading: Apply CVI to daily or weekly charts to gauge broader volatility trends.
Pro tip: Match your timeframe with your trading strategy—scalpers and swing traders will require different chart intervals.
How Do I Reduce False Signals with CVI?
Reducing false signals requires combining CVI with complementary tools and verifying its signals.
- Confirmation Tools: Use trend indicators like Moving Averages or MACD to validate breakout or trend continuation signals.
- Filter Noise: Avoid trading solely based on minor CVI fluctuations, especially in low-volume markets.
Key takeaway: Always confirm CVI signals with market context and additional technical indicators to reduce false positives.
For more tips on minimizing false signals, check this guide to trading strategies.
2. Troubleshooting Errors and Refining Strategies
Misinterpreting Volatility Spikes
- Issue: Traders often mistake volatility increases for trend direction signals.
- Solution: Combine CVI with momentum indicators like RSI or ADX to avoid directional bias.
Struggling with Overfitting Parameters
- Issue: Fine-tuning CVI settings too much can reduce its versatility.
- Solution: Stick to default settings like 10-day or 20-day periods and adapt as needed for specific assets.
Difficulty Integrating CVI Into a Strategy
- Issue: Some traders fail to align CVI with their broader strategy.
- Solution: Treat CVI as a supporting indicator, not a primary signal generator. Combine it with a comprehensive trading plan.
Key takeaway: Regularly review your trading performance and adjust CVI integration based on real-time feedback and results.
Empower Your Trading with CVI FAQs and Solutions
Understanding the Chaikin Volatility Indicator and addressing common pitfalls can significantly enhance your trading success. Regularly revisit and refine your strategy for optimal results.
For further reading, explore Investopedia’s Technical Analysis FAQs.

Conclusion: Mastering the Chaikin Volatility Indicator
1. Recap of the Importance and Utility of CVI
The Chaikin Volatility Indicator (CVI) is a versatile tool for measuring market volatility.
- Key Benefit: It helps traders identify potential breakout points and periods of reduced activity.
- Practical Application: By observing volatility changes, you can anticipate price movements and align trades with market conditions.
Why CVI Matters
Whether you’re a day trader or long-term investor, CVI provides valuable insights into market behavior.
2. Experiment with Settings to Match Your Trading Style
Every trader has a unique style, and CVI can adapt to various strategies.
- Customizable Parameters: Test different lookback periods (e.g., 10-day, 20-day) to find what works for your assets and timeframes.
- Combination Strategies: Combine CVI with complementary tools like Moving Averages, RSI, or volume indicators for improved accuracy.
Pro Tip:
Experiment on a demo account before using CVI strategies in live trading to minimize risks.
For a deeper understanding, explore this resource on customizing indicators.
3. Emphasize Disciplined Trading and Continuous Learning
Success with CVI or any indicator requires discipline and a learning mindset.
- Disciplined Execution: Stick to your trading plan, manage risks effectively, and avoid emotional decisions.
- Continuous Improvement: Analyze your trades, learn from mistakes, and refine your strategies over time.
Final Thought
Trading is a journey of growth. Use tools like CVI to enhance your understanding and align your strategies with market conditions.
For tips on building a disciplined trading approach, check out this guide to disciplined trading.
Terms and Conditions
Educational Purpose
The content provided in this article is intended for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute financial, investment, or trading advice.
Learn how to use the Chaikin Money Flow Indicator to confirm trends, spot divergences, and validate breakouts for smarter trading decisions.


